In today’s world, understanding where our resources come from and how they affect the environment is more important than ever. The terms renewable resources and nonrenewable resources come up frequently in discussions about energy, sustainability, and environmental protection. But what exactly do these terms mean, and why are they so crucial for our future? In this article, we’ll dive deep into the definitions, examples, differences, advantages, challenges, and the global impact of renewable and nonrenewable resources.
What are Resources?
Resources are materials or energy sources found in the environment that humans use to meet their needs. These can be anything from water and sunlight to oil and natural gas. How we use and manage these resources determines how sustainable our lifestyle is for future generations.
Resources are generally categorized into two types:
- Renewable Resources
- Nonrenewable Resources
Let’s explore each in detail.
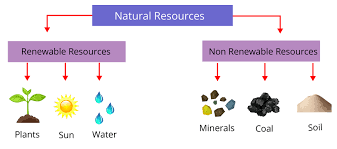
What are Renewable Resources?
Renewable resources are natural resources that can be replenished naturally over short periods of time. These resources are essentially inexhaustible, meaning they won’t run out if managed properly. Some key features include:
- They regenerate naturally.
- They are less harmful to the environment.
- They promote sustainability and conservation.
Examples of Renewable Resources
- Solar Energy: Captured from sunlight and converted into electricity or heat.
- Wind Energy: Generated by harnessing wind power through turbines.
- Hydropower: Produced by the movement of water, typically through dams.
- Geothermal Energy: Comes from the heat stored beneath the Earth’s surface.
- Biomass: Organic material (like wood, crops, and manure) used for fuel.
Advantages of Renewable Resources
- Environmentally Friendly: They produce little or no greenhouse gases.
- Sustainable: As long as the sun shines and the wind blows, these sources are available.
- Job Creation: The renewable energy sector creates millions of jobs globally.
- Energy Independence: Countries can rely on their own natural resources instead of importing fossil fuels.
Challenges of Renewable Resources
- Intermittency: Solar and wind energy depend on weather conditions.
- Storage Issues: Storing energy for when it’s needed (like at night or during calm weather) is still a challenge.
- High Initial Costs: Installing solar panels or wind turbines can be expensive upfront.
What are Nonrenewable Resources?
Nonrenewable resources are natural resources that cannot be replaced within a human timescale. Once they are used up, they are gone forever—or they take millions of years to form again. These resources have powered human civilization for centuries but come with significant environmental costs.
Examples of Nonrenewable Resources
- Coal: A combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock used primarily for electricity generation.
- Oil (Petroleum): Used for fuel, plastics, and chemicals.
- Natural Gas: Mainly methane, used for heating, electricity, and as a chemical feedstock.
- Nuclear Energy: Though uranium is mined and used for nuclear power, it is finite.
Advantages of Nonrenewable Resources
- High Energy Density: Fossil fuels contain a lot of energy in a small amount.
- Reliable and Efficient: Power plants fueled by coal, oil, or gas can run 24/7.
- Well-Established Technology: Infrastructure like pipelines, refineries, and power stations are already in place.
Challenges of Nonrenewable Resources
- Environmental Damage: Extracting and burning fossil fuels releases harmful pollutants and greenhouse gases.
- Finite Supply: These resources will eventually run out.
- Price Volatility: The cost of oil and gas can fluctuate greatly, affecting economies.
Key Differences Between Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources
| Feature | Renewable Resources | Nonrenewable Resources |
| Availability | Inexhaustible (if managed) | Finite, will deplete |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal | Significant |
| Replenishment Time | Short | Millions of years |
| Cost Trends | Decreasing | Increasing (scarcity) |
| Examples | Solar, Wind, Biomass | Oil, Coal, Natural Gas |
| Sustainability | Highly sustainable | Unsustainable in the long term |
The Global Impact of Resource Usage
How we use renewable and nonrenewable resources shapes the world we live in today and the world we will leave for future generations.
Environmental Impact
Nonrenewable resources contribute heavily to climate change, air pollution, water contamination, and habitat destruction. Carbon emissions from burning fossil fuels are the main cause of global warming, leading to melting ice caps, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events.
Renewable energy, while much cleaner, is not without impact. Large hydroelectric dams can disrupt ecosystems, and manufacturing solar panels requires mining raw materials. However, overall, renewables offer a much lower environmental footprint.
Economic Impact
Countries rich in fossil fuels often experience economic booms, but their economies can suffer when prices drop or resources deplete. In contrast, investment in renewable energy offers more stable, long-term growth opportunities and reduces dependency on a volatile global oil market.
Social Impact
Access to affordable, reliable energy improves quality of life, boosts education, healthcare, and economic opportunities. Transitioning to renewable energy can also help address issues of energy poverty in underdeveloped regions.
The Transition to Renewable Energy
The world is currently undergoing a massive energy transition, often referred to as the “energy revolution.” Many countries are setting ambitious targets to reduce their carbon emissions and increase the share of renewables in their energy mix.
Steps Being Taken
- Government Policies: Incentives like tax breaks for installing solar panels and investment in research and development.
- Corporate Action: Many large companies are committing to using 100% renewable energy.
- Technological Innovations: Improvements in battery storage, energy efficiency, and smart grids are making renewable energy more viable.
Challenges Ahead
- Infrastructure Needs: Modernizing power grids to handle decentralized renewable energy sources.
- Political Will: Shifting policies, especially in fossil-fuel-dependent nations.
- Public Awareness: Educating communities about the benefits and addressing misconceptions.
How Students Can Make a Difference
At Study Rhino, we believe that young people are powerful agents of change. Here’s how students can contribute to a more sustainable future:
- Learn and Share: Educate yourself and others about renewable and nonrenewable resources.
- Advocate: Support policies and leaders that prioritize clean energy and sustainability.
- Reduce Personal Carbon Footprint: Use energy-efficient appliances, reduce car usage, and recycle.
- Innovate: Pursue studies and careers in environmental science, renewable energy, and sustainable design.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources is fundamental to creating a sustainable future. While nonrenewable resources have powered incredible technological advancements, they come at a high environmental cost and will not last forever. Renewable resources offer a cleaner, more sustainable path, but they require investment, innovation, and collective effort.
The choices we make today—whether at the personal, community, or government level—will determine the health of our planet for generations to come. At Study Rhino, we are committed to empowering students and learners everywhere to be part of the solution. Together, we can build a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable world.